Indonesia: 2020 GDP expected to contract by 2.0%
Prospects for a quick economic recovery are weighed down by Covid-19
Lockdowns and slowdowns
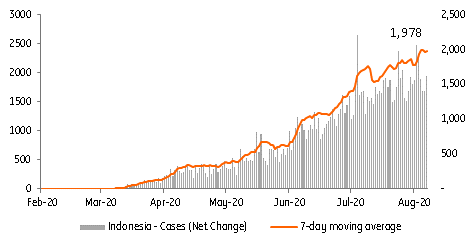
Indonesia implemented “large scale social restrictions” (PSBB) on 10 April in the capital Jakarta and neighbouring regions to help limit the spread of the Covid-19 virus. Originally slated to end on 5 June, authorities were forced to implement a phased removal of restrictions as new daily Covid-19 infections continued to rise. As of 13 August, the official total number of Covid-19 cases in Indonesia was 130,718 while the 7-day moving average for daily new infections remains elevated at 1,978 cases.
GDP contraction expected in 3Q
PSBB and the negative impact on economic activity will force 3Q GDP into contraction and should weigh on recovery efforts in the coming quarters.
Finance Minister Indrawati currently expects the economy to enter a recession by 3Q as PSBB stifles overall economic activity. Indrawati, however, forecasts a recovery of up to 2.2% growth in the second half with positive growth by 4Q as the economy reopens and government outlays accelerate after only disbursing roughly 20% of the total Covid-19 stimulus package.
Forward-looking indicators, however, point to a prolonged downturn and we expect 2020 GDP to drop to -2.0% from 5.0% in 2019 with growth momentum subdued in the coming quarters as Indonesia struggles to contain the spread of Covid-19.
Indonesia GDP and forecasts (%)

PSBB knocks out 2Q GDP
GDP contracted in the second quarter as large scale social restrictions that curbed mobility (PSBB) limited household consumption, which comprises roughly 55% of total GDP. Meanwhile, government spending has been modest so far. President Jokowi has ordered an acceleration in outlays with only 20% of the total IDR695.2 trillion rescue plan spent so far. 2Q GDP contracted by 5.3% with a broad-based slowdown in economic activity reflected in cratering car sales (96% drop in May to 3,551 units) and much-weaker retail sales falling by 20.6% and 14.4% in May and June, respectively.
Indonesia Covid-19 cases and 7-day moving average
Economic data improves but still far from pre-pandemic levels
Recent forward-looking indicators show a slight improvement after plunging to multi-year lows recorded during the PSBB in April. The modest improvement in data, however, remains well-below levels posted prior to Covid-19 and thus we do not expect a quick and sustained recovery in the near term. A recent poll conducted by Indikator Politik Indonesia showed more than 60% of respondents were in favour of reopening the economy as soon as possible, despite the sustained rise in Covid-19 infections. The survey may indicate the severe economic impact on individuals, which was also reflected in downbeat consumer sentiment. Sentiment improved to 83.8 in June, but it is still much lower than pre-pandemic levels when consumer confidence averaged 122.8 in the two months before the lockdown.
Indonesia consumer confidence

PMI improves but remains in contraction
Despite a pick-up in exports in June, manufacturing activity remains in contraction with the July manufacturing PMI report at 46.9. The July reading is an improvement from the levels in May and June, but still below the 49.4 average recorded in the 12 months prior to the implementation of PSBB in April.
Indonesia PMI manufacturing

Covid-19 weighs on prospects for a quick recovery
Despite government projections for a quick recovery, we continue project a contraction in 3Q and below-average 4Q GDP as household retail sales remain downbeat and PMI manufacturing stays in contraction. We do not see a quick turnaround in the economic prospects for Indonesia given the still rampant spread of Covid-19 in the country.
New daily infections remain on an uptrend and are likely to weigh on consumer sentiment and investment activity
New daily infections remain on an uptrend and are likely to weigh on consumer sentiment and investment activity in the months to come while bureaucratic red tape may hinder the government’s efforts to disburse the Covid-19 stimulus funds quickly. Thus, even if we have seen a slight improvement in economic data of late, we believe that GDP is likely to contract for at least another quarter with a return to pre-pandemic economic momentum not likely in the near term as Indonesia struggles to contain the virus.
ING GDP forecasts (%)

Download
Download article
17 August 2020
Good MornING Asia - 17 August 2020 This bundle contains {bundle_entries}{/bundle_entries} articles"THINK Outside" is a collection of specially commissioned content from third-party sources, such as economic think-tanks and academic institutions, that ING deems reliable and from non-research departments within ING. ING Bank N.V. ("ING") uses these sources to expand the range of opinions you can find on the THINK website. Some of these sources are not the property of or managed by ING, and therefore ING cannot always guarantee the correctness, completeness, actuality and quality of such sources, nor the availability at any given time of the data and information provided, and ING cannot accept any liability in this respect, insofar as this is permissible pursuant to the applicable laws and regulations.
This publication does not necessarily reflect the ING house view. This publication has been prepared solely for information purposes without regard to any particular user's investment objectives, financial situation, or means. The information in the publication is not an investment recommendation and it is not investment, legal or tax advice or an offer or solicitation to purchase or sell any financial instrument. Reasonable care has been taken to ensure that this publication is not untrue or misleading when published, but ING does not represent that it is accurate or complete. ING does not accept any liability for any direct, indirect or consequential loss arising from any use of this publication. Unless otherwise stated, any views, forecasts, or estimates are solely those of the author(s), as of the date of the publication and are subject to change without notice.
The distribution of this publication may be restricted by law or regulation in different jurisdictions and persons into whose possession this publication comes should inform themselves about, and observe, such restrictions.
Copyright and database rights protection exists in this report and it may not be reproduced, distributed or published by any person for any purpose without the prior express consent of ING. All rights are reserved.
ING Bank N.V. is authorised by the Dutch Central Bank and supervised by the European Central Bank (ECB), the Dutch Central Bank (DNB) and the Dutch Authority for the Financial Markets (AFM). ING Bank N.V. is incorporated in the Netherlands (Trade Register no. 33031431 Amsterdam).
