EUR & ECB crib sheet: A half-point hike is not good news for the euro
We expect the European Central Bank (ECB) to hike by 50bp at its September meeting. Markets are pricing in 66bp at the moment, and the consensus is leaning in favour of 75bp, so we see some downside risks for the euro. At the same time, short-term rates have not had much of an impact on EUR/USD lately, and the energy crisis should remain the key driver
Four scenarios ahead of the September ECB meeting
As discussed in our September ECB preview, policymakers in Frankfurt will likely have to choose between a 50bp or 75bp rate hike this week. We think that a 75bp move would be too hard to digest for the dovish front within the Governing Council, and our call is for a 50bp move. That said, we cannot fully exclude a 75bp hike aimed at frontloading tightening before a recession hits this winter.
In our “Crib Sheet”, we analyse four potential scenarios on a scale from dovish to ultra-hawkish and what this can mean for EUR/USD and EUR rates, taking into account the size of the rate hike as well as the ECB’s stance on inflation, growth and quantitative easing/tightening (QE/QT).
EUR and ECB crib sheet
Downside risks for EUR…
The market’s pricing for the meeting is currently around 66bp, which by itself suggests some negative reaction by the EUR if our 50bp call proves correct. Much of the market reaction will also be driven by any hints about future policy.
Since a reiteration of the meeting-by-meeting, data-dependent approach seems quite likely, markets will have to derive their rate path expectations from the updated staff projections on growth and inflation. In particular, the size and length of a winter recession will be key, and should it become the ECB’s baseline scenario, then some dovish re-pricing across the curve might occur and weigh on the euro.
Comments about the euro weakness are likely to be a theme too and could have some impact on the EUR. However, verbal protest about a weak currency is now the norm among many central banks and has notably yielded very few results. Unless any reference to FX interventions is made, markets may not read too much into currency-related comments.
… but the ECB is a secondary driver now
Regardless of the direction of the EUR reaction on Thursday, there’s a non-negligible chance that the FX impact will prove rather short-lived. This is because EUR/USD has been blatantly unreactive to ECB rate expectations lately, as the energy crisis has continued to drive the majority of the pair’s moves. In the chart below, we show how the two-year EUR-USD swap rate differential – a gauge of ECB-Fed monetary policy divergence expectations – has moved significantly in favour of the EUR recently, but EUR/USD has failed to follow it higher.
EUR/USD hasn't followed the short-term rate differential higher
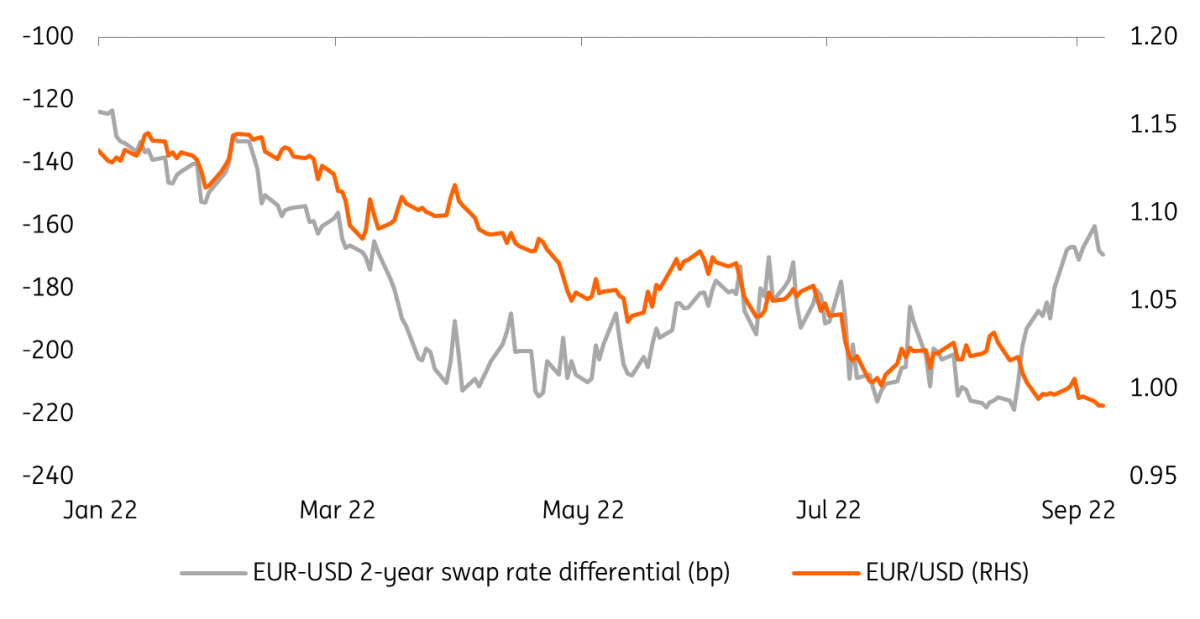
In our EUR/USD short-term fair value model, the short-term rate differential now has a smaller beta than relative equity performance, which is a gauge of diverging growth expectations and is more directly impacted by the energy crisis. This also means that the short-term undervaluation in EUR/USD has shrunk to around 3-4% from the 5-6% peak seen two weeks ago.
We expect the energy story to return firmly to the driving seat for EUR/USD after the post-ECB reaction. Barring a very hawkish surprise, this should keep EUR/USD below parity and prevent it to reconnect with the more supportive rate differential. The 0.98-0.99 area could prove to be a near-term anchor for EUR/USD, but a further worsening of the energy crisis and/or further dollar strengthening can trigger a drop to the 0.96-0.97 area.
This publication has been prepared by ING solely for information purposes irrespective of a particular user's means, financial situation or investment objectives. The information does not constitute investment recommendation, and nor is it investment, legal or tax advice or an offer or solicitation to purchase or sell any financial instrument. Read more
