Japan’s exports and core machinery orders recover
Japan’s trade deficit widened in July as imports surged due to high commodity prices while forward looking core machinery orders rebounded in June. Today's data supports our view that GDP will likely continue to rise in the current quarter led by investment, but at a slower pace than the previous quarter
| 19.0% |
ExportsYear-on-year |
| Higher than expected | |
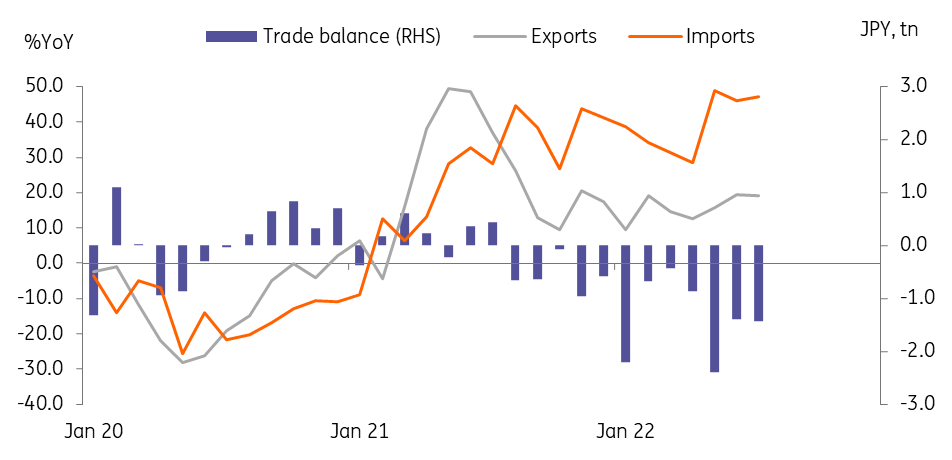
Imports grew faster than exports, deepening the trade deficit in July
Exports rose 19.0% year-on-year in July (vs 19.4% in June), a bit higher than the market consensus of 17.6%. Auto exports to the US and semiconductor exports to China were particularly strong. Meanwhile, imports jumped 47.2% in July (vs 46.1% in June), also above the consensus forecast of 45.5%, mainly led by the high cost of commodities.
Still, as global oil prices have dropped since June, we expect the trade deficit to narrow, with import growth decelerating. Also, auto exports are expected to improve as the production of other major automakers continues to increase. Thus, the contribution of net exports to GDP will likely record a small gain in 3Q (vs 0.0% in 2Q).
Trade deficit widened in July
Core machinery orders rebounded slightly in June
A leading indicator of capital spending, core machinery orders rose 0.9% month-on-month seasonally-adjusted in June (vs -5.6% in May), slightly missing the market consensus of 1.0%. In the second quarter, core machinery orders rebounded firmly by 8.1% quarter-on-quarter sa (vs -3.6% in the first). Thus, we expect Capex investment to improve in the rest of this year, with growth momentum slowing gradually. Auto and electrical machinery orders increased as global supply bottlenecks and China lockdowns eased while semiconductor manufacturing equipment orders fell for the first time in three months.
This publication has been prepared by ING solely for information purposes irrespective of a particular user's means, financial situation or investment objectives. The information does not constitute investment recommendation, and nor is it investment, legal or tax advice or an offer or solicitation to purchase or sell any financial instrument. Read more
Download
Download snap