Indonesia: Imports bounce back after long slump
Indonesia’s imports recorded their first expansion since mid-2019, hinting at possible economic recovery
| 14.9% |
Import growth1st expansion since June 2019 |
Exports sustain growth while imports recover
Indonesia’s export sector has continued to hum along, posting a 4th straight month of expansion with global economic prospects brightening as vaccination efforts continue for developed and emerging markets alike. Meanwhile, imports recorded their first expansion after 19 straight months of contraction, which could point to a possible gradual improvement in domestic economic activity and resumption of capital build up ahead of an economic recovery. Despite the sharp pickup in imports (+14.9%), the trade balance remained in surplus of $2.0 bn, with exports posting a 8.6% gain in February.
Indonesia trade balance
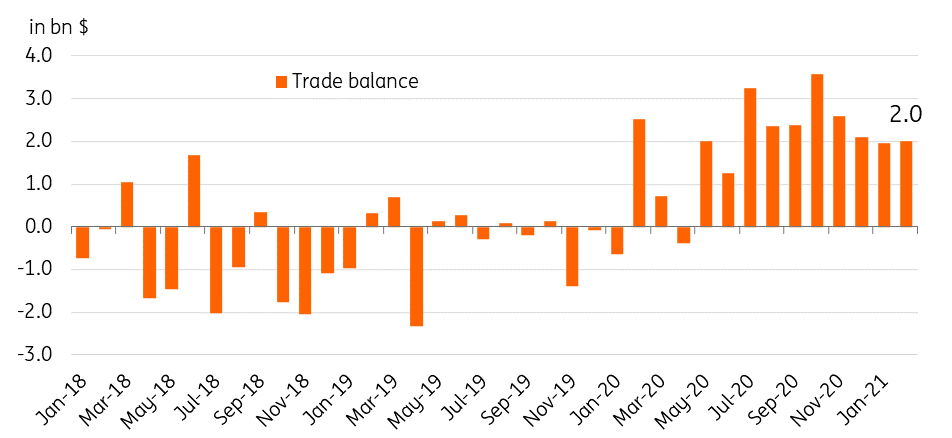
Trade trends hint at recovery?
In the coming months, exports might sustain their expansion with demand for commodities such as iron and steel likelly to accelerate in line with expectations for faster global growth. A continued improvement in export trends will bode well for Indonesia’s growth prospects as manufacturing activity improves, which in turn would help offset job losses during the pandemic. Meanwhile imports, which finally recorded an expansion after an extended slump, may also sustain their growth as the economy gradually recovers after last year’s contraction. The bounce in imports can be traced to an increase in inbound shipments of capital goods (machinery and electrical equipment) suggesting that investment outlays me be returning. If these trade trends continue, we can expect a positive boost to economic recovery prospects in the coming months as the economy aims to exit its ongoing recession as soon as 2Q 2021. Meanwhile, a strong showing for exports coupled with a modest gain in imports may continue to provide a trade surplus that would be supportive for IDR in the near term, and partially offset recent pressure induced by the sharp adjustment in global bond yields.
This publication has been prepared by ING solely for information purposes irrespective of a particular user's means, financial situation or investment objectives. The information does not constitute investment recommendation, and nor is it investment, legal or tax advice or an offer or solicitation to purchase or sell any financial instrument. Read more
Download
Download snap