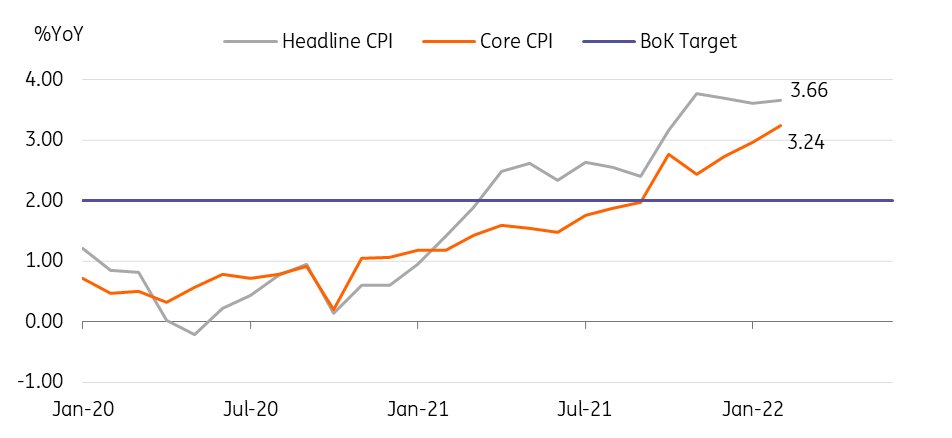
Korea: February CPI accelerated to 3.7%YoY
Inflationary pressures have built up across the board with the core CPI excluding agricultural products and oils rising to 3.2% (vs 3.0% in January).
| 3.7% |
Headline CPI inflationFebruary |
| Higher than expected | |
The rise of the consumer price index in February was driven by higher energy prices and personal services
Headline CPI inflation accelerated to 3.7% YoY in February (vs. 3.5% in January), in line with ING's forecast but above the market consensus (3.5%). Industrial goods rose 5.2%YoY (vs 4.2% in January), with a 19.4% rise in fuel, but fresh-food prices dropped -0.9%, marking the first drop in four months. Utilities such as electricity, water & gas were unchanged at 2.9% after making a significant price adjustment in January.
In terms of services inflation, rentals for housing stayed at 2.1%YoY for the second month - the recent household credit tightening measures probably played a role. Personal services inflation jumped to 4.3% with a notable gain in eating-out services (6.2%).
Inflation on the rise
Policy reactions to curb the fast inflation growth are expected
To mitigate the impact on high energy prices, the government decided to extend the current 20% fuel tax cut for three more months until the end of July and might consider a steeper tax cut if oil prices rise further.
Given that Dubai Crude oil prices recently hit $110 per barrel, upward pressure is highly likely in the foreseeable future. Even though the Bank of Korea took a pause last month, if CPI inflation hits 4%, then we expect the BoK to immediately respond by hiking rates again.
This publication has been prepared by ING solely for information purposes irrespective of a particular user's means, financial situation or investment objectives. The information does not constitute investment recommendation, and nor is it investment, legal or tax advice or an offer or solicitation to purchase or sell any financial instrument. Read more
Download
Download snap