Thailand: Negative inflation gains traction
But the Bank of Thailand’s rate policy has almost reached its limits, which together with the divide among BoT policymakers over the last 25 basis point rate cut in May, points to the end of the easing cycle
| -3.4% |
CPI inflation in MayYear-on-year |
Steeper inflation fall
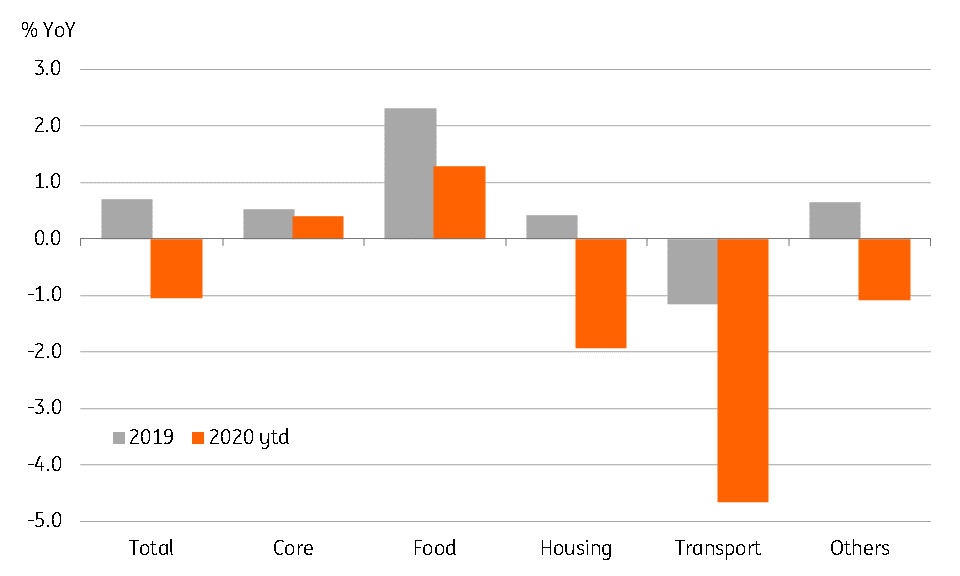
The streak of negative inflation in Thailand gained further traction in May. CPI inflation fell to -3.4% year-on-year last month, steeper than the consensus of -3.2% though not as bad as our -4.2% forecast. This follows a -3.0% reading in April. Core CPI inflation slowed to 0% from 0.4% in April.
Housing and transport prices remained the main sources of falling inflation, though at -5.4% YoY and -9.2%, respectively, inflation in these components was little changed from readings in April. As we expected, food prices were an added source, with a fall to 0% from 1% on the back of the high base effect.
Technical deflation
This marks the third consecutive month of negative inflation in Thailand, which the director-general of the Commerce Ministry’s trade policy and strategy office, Pimchanok Vonkorpon, noted as “technical deflation”. He expects full-year average inflation in 2020 of between -0.2% to -1.0% (year-to-date -1.0%), which implies there would be much smaller declines in the rest of the year than the -3% currently. We are sceptical of such a prospect.
We expect inflation in the rest of the year to stay around -3% and the full-year average to come in at -2.3%, the worst annual rate in decades.
CPI Inflation (% year-on-year)
Improved confidence
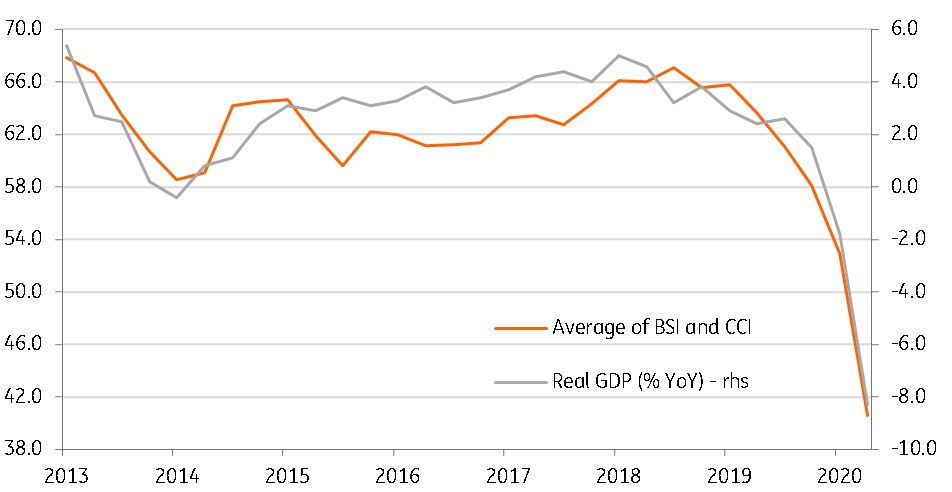
Also released today, the Consumer Confidence Index (CCI) rose to 48.2 in May from a record low of 47.2 in April. Coming on the heels of a pick-up in the Business Sentiment Index (BSI) in the month (to 34.4 from 32.6), the data reflects a stabilising Covid-19 situation and gradual relaxation of movement restrictions.
However, these indexes still correspond to our forecast of a record GDP contraction in the current quarter, by 8.3% YoY (see chart).
Weak confidence, weak GDP growth
What all this means for policy?
Falling inflation supports the argument for more Bank of Thailand (central bank) monetary easing. However, a total 75 basis point BoT rate cut so far this year has taken the policy rate to an all-time low of 0.50%, from where there isn’t much space for it to fall further. Moreover, the divide among policymakers over the latest 25bp cut on 20 May, with some favouring no change, points to the end of the easing cycle.
With rate policy reaching its limits and the government going on a borrowing spree to fund huge fiscal stimulus, the idea of unconventional or quantitative easing (QE) has been floating around. We don’t see the BoT moving to that path in the near-term.
This publication has been prepared by ING solely for information purposes irrespective of a particular user's means, financial situation or investment objectives. The information does not constitute investment recommendation, and nor is it investment, legal or tax advice or an offer or solicitation to purchase or sell any financial instrument. Read more
Download
Download article
4 June 2020
Good MornING Asia - 5 June 2020 This bundle contains 4 Articles