Sweden prepares for 75bp rate hike despite house price correction
For now, higher-than-expected inflation data trumps the mounting concerns about the housing market for the Riksbank. A 75bp rate hike looks likely on Thursday, and we expect one final 50bp increase in February
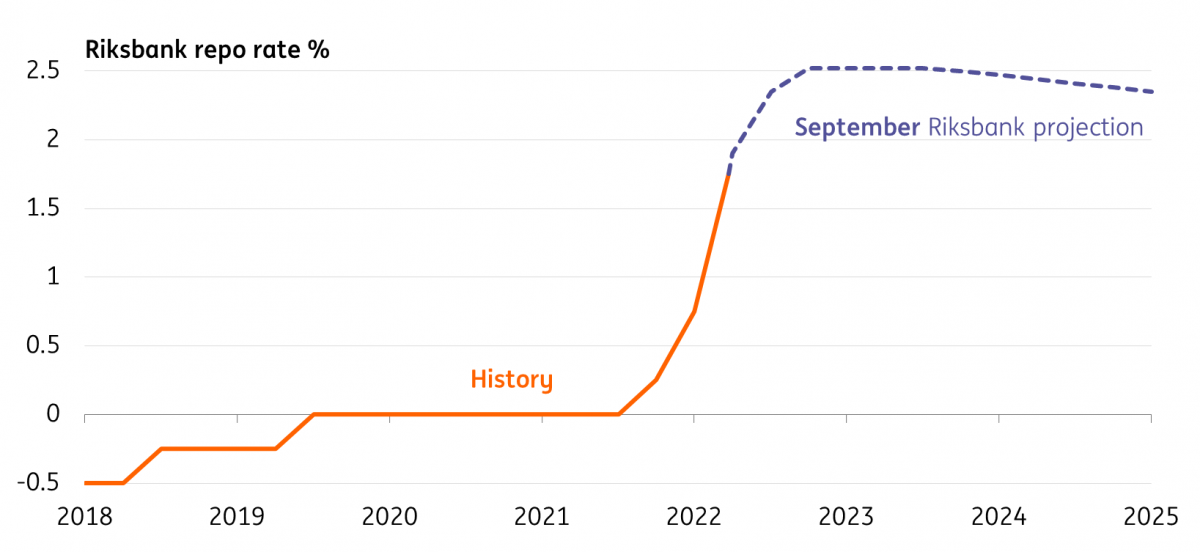
The Riksbank is likely to hike faster than signalled in September
When the Riksbank hiked its policy rate by a full percentage point back in September, it was coupled with a message that this was unlikely to happen a second time. The bank’s forecasts pointed to a peak policy rate of 2.5% in April, effectively setting the stage for a 50bp hike this week. But in what has become a familiar tale for central banks, core inflation has since come in higher than the Riksbank had anticipated, and a more aggressive move now looks likely.
The Riksbank's September rate hike projection
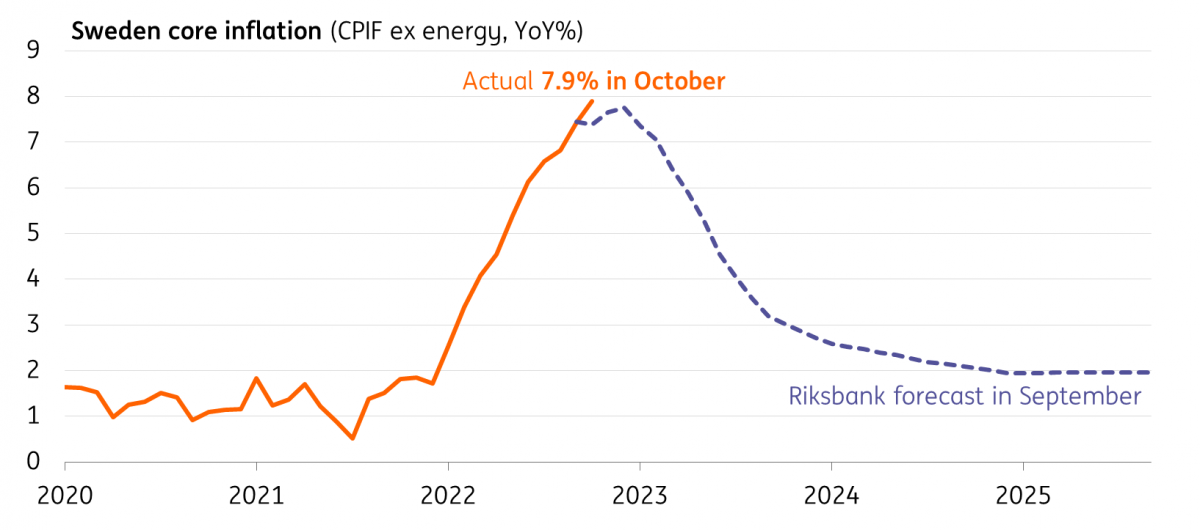
At 7.9%, core CPIF is half a percentage point above the central bank’s September forecast. The jobs market still looks strong, too, even if we saw an unexpected rise in the unemployment rate in the latest set of data (these numbers are fairly volatile). Together with the weak krona, it looks like policymakers will opt for a 75bp rate rise on Thursday. We’re forecasting that rates peak at 3% in February.
Core inflation rose from 7.4% to 7.9% in October
Riksbank is keen to stay ahead of the ECB, but housing is a risk
All of this is reinforced by the recent messaging we’ve had from Swedish policymakers. Among the Riksbank’s hawks, Governor Stefan Ingves has stressed the importance of staying a “comfortable distance” ahead of the European Central Bank. Don’t forget that Thursday’s meeting is the last before February, and the ECB will meet – and presumably hike rates – twice before then. Ingves said in the last set of meeting minutes that the Riksbank would need to “follow along upwards at the same pace” at the very least.
However, there are good reasons to think the Riksbank is not very far away from the end of its tightening cycle, and the most obvious of these is the housing market. It’s no secret that Sweden’s economy is among the more interest-rate sensitive, and there are already signs that tighter policy is weighing on the housing market. Transaction volumes have fallen sharply, and by some measures, property prices have already started to fall. The headline Valueguard HOX housing index fell a further 3% in October alone, and the Riksbank has projected more declines to come. Much of Sweden’s mortgage market is either fixed for short periods or not at all.
Housing market is declining at a faster pace than expected
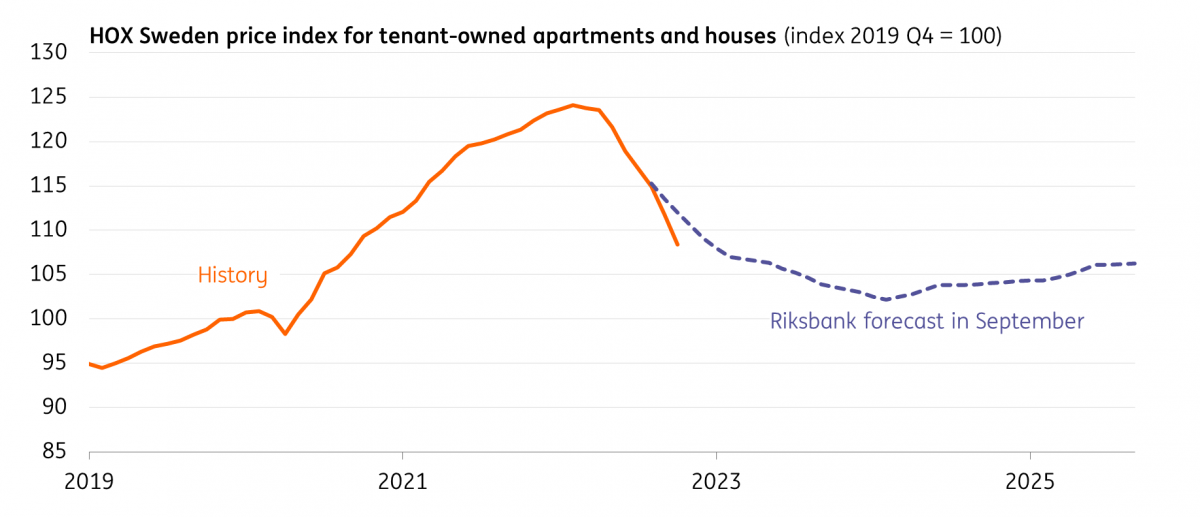
In short, there’s a growing trade-off for the Riksbank between taming inflation and exposing debt fragilities – a challenge that’s far from unique to Sweden. We expect the Riksbank’s new rate projections to factor in a further 25-50bp of tightening next year, and much will depend on the outcome of wage negotiations in the spring.
A stronger SEK still unlikely in the near term
The SEK OIS curve is embedding around 60bp of tightening this week, so a 75bp move would likely come as a hawkish surprise. However, we believe a greater focus will be on the new rate projections, which are (unlike in Norway) hardly ever followed to the letter by investors, but will provide an indication of how much appetite there is for further tightening. Implicitly, the projections will also show how much the focus is shifting from the mere inflation-fighting exercise to domestic concerns – in particular on housing. This is important because it will shape how SEK rates react to future data releases.
On the FX side, despite the Riksbank’s constant protests against a weak krona, the implications of monetary policy remain rather limited for the near term, where we see EUR/SEK trading around 11.00 and facing upside risks. The RB’s hawkishness has been ineffective at lifting SEK in an unstable risk environment, especially in Europe, and we doubt this will change any time soon.
The actual implications may emerge in the longer run. If the RB ends up hiking substantially more than the ECB by the time both central banks’ tightening cycles come to an end, then EUR/SEK may face some downward pressure next year, but only under the condition that risk sentiment stabilises.
As discussed in our 2023 FX Outlook, we expect SEK to remain vulnerable on the back of European and global risk factors, and only expect limited downside risks for EUR/SEK into end-2023 despite a widening in the Riksbank-ECB rate differential. We currently forecast 10.40/50 for the pair in 2H23.
This publication has been prepared by ING solely for information purposes irrespective of a particular user's means, financial situation or investment objectives. The information does not constitute investment recommendation, and nor is it investment, legal or tax advice or an offer or solicitation to purchase or sell any financial instrument. Read more
Download
Download article