Malaysia: Downgrade of inflation, BNM policy forecasts
We revise our 2018 inflation forecast for Malaysia to 1.8% from 2.4%. We no longer expect the central bank (BNM) to change policy later this year
| 1.4% |
April CPI inflationYear-on-year |
| Lower than expected | |
Persistent low inflation
Malaysia’s consumer price index rose by 1.4% year-on-year in April, slower than the consensus of 1.6% but slightly up from 1.3% in March which was the lowest inflation rate in almost two years. Food remained the main inflation driver albeit at a slower year-on-year rate of increase of 2.6% than the 2.8% recorded in March. Low base effects swung the change in the transport component, the other main CPI driver, to positive from negative over the same months, but the effect was less pronounced than anticipated. Inflation in most other components was little changed, while core inflation slowed to 1.5% from 1.7%.
The Ramadan-related increase in food prices will add to CPI inflation pressure over the coming months (this year Ramadan is from 17 May to 14 June). However, with the Goods and Services Tax in Malaysia to be set at zero starting this June, any inflation spike will be transitory. The GST will be replaced by a less severe Sales and Services Tax, though there is no clarity on the timetable for this move.
We expect inflation to remain well under 2%, the low end of the central bank’s (Bank Negara Malaysia) 2-3% forecast, over the rest of the year. We are revising down our full-year 2018 inflation forecast to 1.8% from 2.4%. The consensus forecast of 2.9% looks way out of date.
Stable central bank policy
BNM started withdrawing policy accommodation earlier this year with a 25bp hike in the overnight policy rate to 3.25% in January. The latest inflation data together with a downward GDP growth surprise in the first quarter and prospects of further softening of both growth and inflation ahead, lead us to revise our BNM policy forecast from one more 25bp rate hike in the third quarter to no more hikes this year.
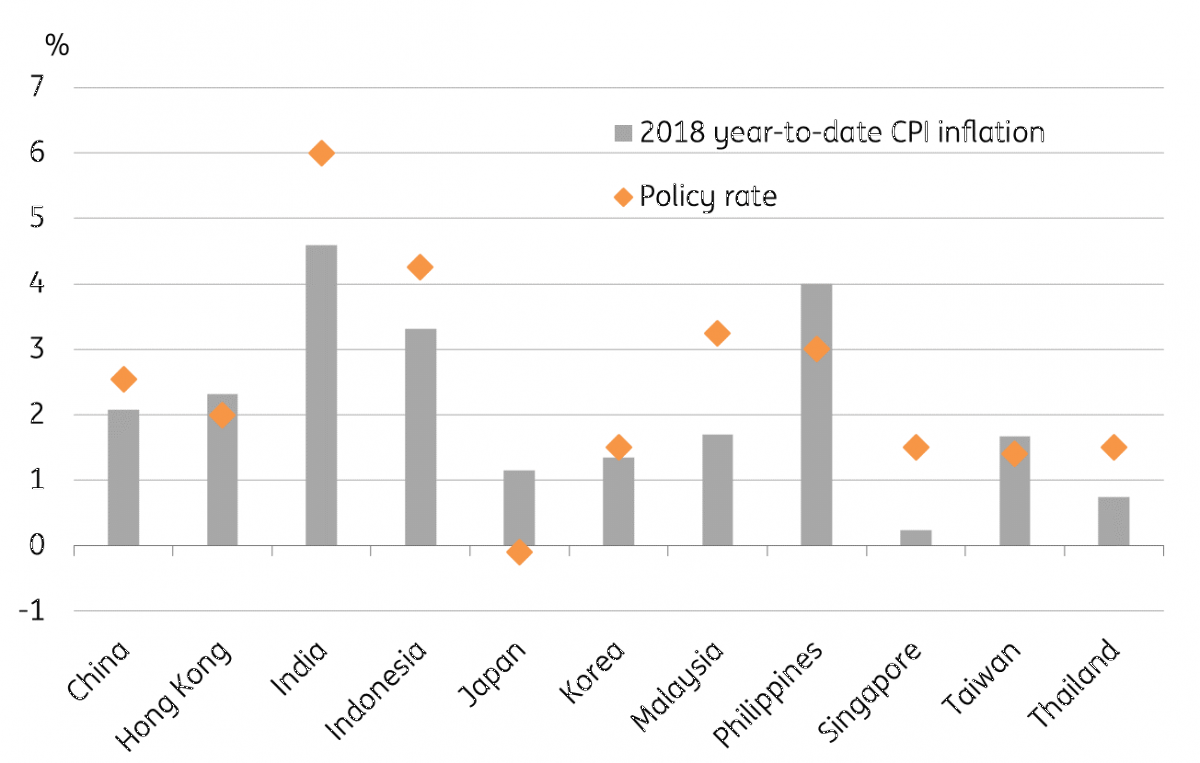
Real interest rates in Malaysia are relatively high compared with most other Asian economies (see figure), suggesting that BNM not mechanically following the Fed with rate-hikes, will not do much harm to investor confidence towards local financial assets, especially the Malaysian ringgit (MYR). But pending clarity on economic policy under the new government, the MYR is likely to remain under weakening pressure. We see the currency soon testing the 4.00 level against the USD. Our USD/MYR forecast for end-2018 is 4.05 (spot 3.98).
Asian central bank policy space
This publication has been prepared by ING solely for information purposes irrespective of a particular user's means, financial situation or investment objectives. The information does not constitute investment recommendation, and nor is it investment, legal or tax advice or an offer or solicitation to purchase or sell any financial instrument. Read more
Download
Download article
23 May 2018
Good MornING Asia - 24 May 2018 This bundle contains 2 Articles