Malaysia: Inflation misses estimates, again
Based on strong growth and benign inflation trends, we still look for Malaysia's central bank, Bank Negara Malaysia, to raise rates later this year
| 1.4% |
CPI inflation in FebruaryYear-on-year |
| Lower than expected | |
Food, housing, transport drag inflation lower
Malaysia’s consumer price inflation slowed more than expected to 1.4% year-on-year in February from 2.7% in January (consensus 1.9%, ING forecast 1.7%). It’s no surprise that the food and transport CPI components continued to slow, thanks to the favourable base effects in both. Lower housing prices also helped despite seasonal quarterly hikes in rentals in the last month. Core inflation, which strips out food and fuel-related components from the total CPI, also slowed to 1.8% in February from 2.2% in January.
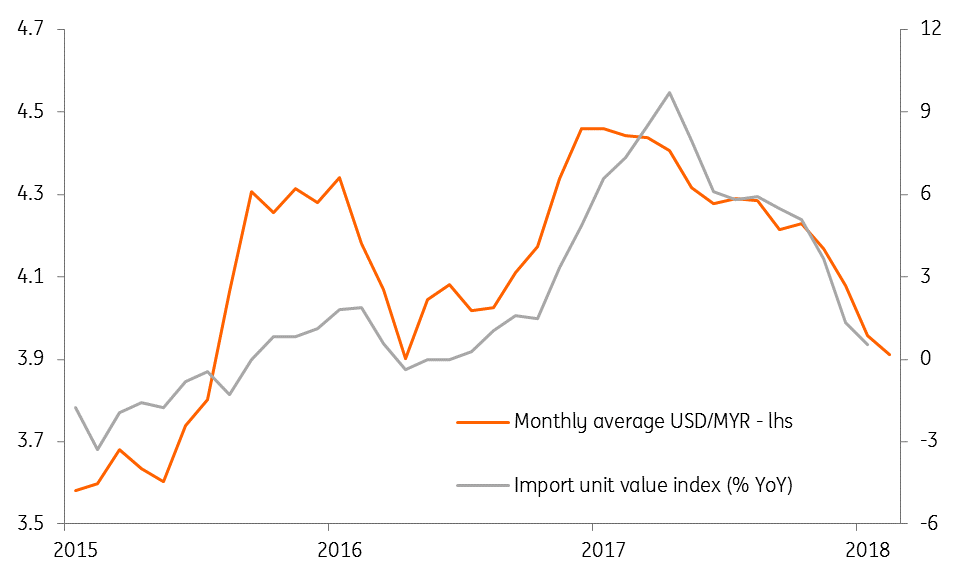
Among other inflation drivers, steadily falling inflation of import prices reflects the impact of continuing strength of the Malaysian ringgit (MYR) whereas the impact of rapid growth in domestic wages on consumer prices continues to be muted.
Strong currency, low imported inflation
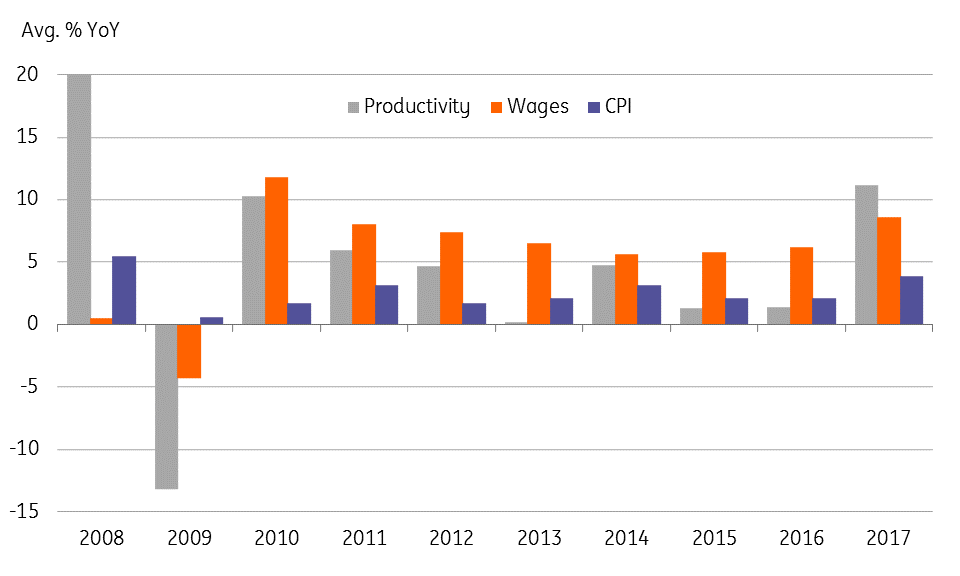
Tight labour market has no impact on inflation
The tight labour market with wage growth outpacing productivity growth since September could be potentially inflationary. Or, it may not be. 2017 was the first year in almost a decade in which annual average wage growth slowed below productivity growth and yet inflation accelerated (see chart). History teaches us that the supply-side push to prices, especially in food and fuel sectors, is more dominant than demand-side pressures in driving Malaysia’s inflation. Without any such supply shocks from food or oil prices, inflation will not be a concern throughout 2018.
Productivity, wages and inflation
Policy mix remains positive for Malaysian ringgit
Based on strong growth and benign inflation trends, we still look for Malaysia's central bank, Bank Negara Malaysia, to raise rates later this year, once the elections are out of the way. The macro policy mix of tightening monetary and loose fiscal policy is favourable for the Malaysian ringgit (MYR) to sustain its position among Asia’s outperformers this year. The MYR’s 3.3% year-to-date appreciation against the US Dollar is the second-best among Asian currencies. Our end-2018 USD/MYR forecast is 3.72 (spot 3.92, consensus 3.83).
This publication has been prepared by ING solely for information purposes irrespective of a particular user's means, financial situation or investment objectives. The information does not constitute investment recommendation, and nor is it investment, legal or tax advice or an offer or solicitation to purchase or sell any financial instrument. Read more
Download
Download article
21 March 2018
Good MornING Asia - 22 March 2018 This bundle contains 5 Articles