Bank of England to stick to 50bp rate hike despite the Fed and ECB doing more
The prospect of lower near-term inflation takes some of the pressure off the Bank of England to move even more aggressively on Thursday. We expect a second consecutive 50 basis point rate hike, although it's a close call between that and a 75bp move
Our Bank of England call
We narrowly favour a 50bp hike on Thursday, taking the Bank Rate to 2.25%, although 75bp is clearly on the table and we would expect at least a couple of policymakers to vote for it. It's even possible we get a rare three-way vote – the first since 2008 – if dovish committee member Silvana Tenreyro votes for a 25bp hike as she did in August. If our call is correct, then we expect another 50bp move in November and at least another 25bp in December. That would take Bank Rate to the 3% area.
It's a tough meeting to call...
Next week’s Bank of England meeting is crucial. It will tell us not only how worried policymakers are about the slide in sterling and other UK markets, but also how the government’s decision to cap household/business energy prices will translate into monetary policy.
It has also, undeniably, become a close meeting to call. Hawks at the Bank of England will undoubtedly be concerned about the independent sterling weakness we've seen recently (down 4% in trade-weighted terms), even if in practice it’s unlikely to make a huge difference to the big-picture inflation outlook. Both the Fed and ECB will have also done (at least) 75bp hikes by Thursday, and markets are increasingly concluding the BoE will do the same.
But we’d caution against assuming UK policymakers will ramp up the pace of rate hikes simply because that’s what everyone else is doing – or indeed because that’s what markets are pricing. As recently as June, the BoE hiked by ‘only’ 25bp, despite the Fed having done 75bp the night before, and defying market expectations for more.
Indeed, there are good reasons to think the Bank will ‘stick to its guns’ and simply repeat the 50bp hike it executed in August.
Government energy price guarantee means inflation unlikely to go much higher
One immediate consequence of the government’s decision to cap household electricity/gas bills this winter is that headline inflation should be dramatically lower. We now expect CPI to peak at 11% in October, only slightly above where it is now, compared to 16% in January had the government not intervened. It also means headline inflation should be back around the BoE’s 2% target at the end of next year, crazy as that sounds. All of that should help keep consumer inflation expectations in check, and in fact, we’ve already seen a noticeable pullback in long-term price expectations according to the latest BoE survey.
Admittedly there appears to be a wide range of views at the BoE about how much all of this actually matters. But we know from recent comments, notably from hawk Catherine Mann, that some policymakers have had a keen eye on consumer expectations over recent months.
By the BoE's own measure, consumer inflation expectations have dipped
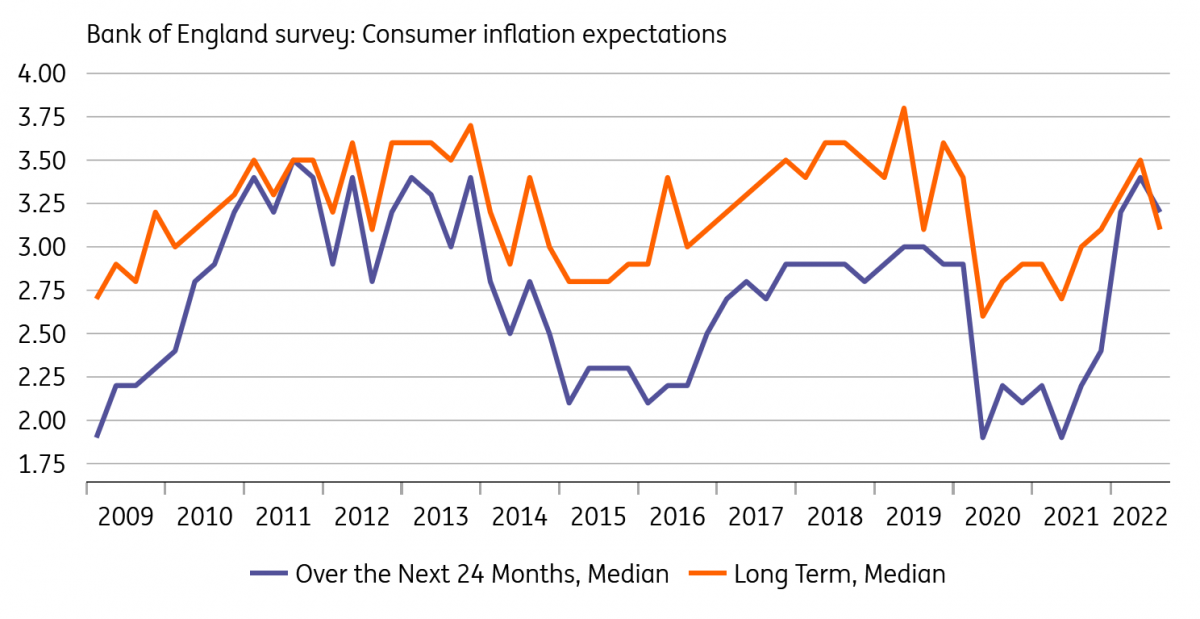
The flip side, of course, is that extra government support potentially means higher medium-term inflation, even if headline rates are lower in the very near term. We think this is ultimately what most committee members will be more interested in.
The hit to GDP this winter is likely to be more moderate than the 2% cumulative decline the BoE forecast in August, while the sharp rise in unemployment it projected is less likely to materialise too. With worker shortages proving to be a long-running issue in the jobs market, the risk is that higher wage growth could become a persistent feature that requires more central bank tightening.
That doesn't necessarily have to manifest itself as a radically higher policy rate, and we still believe investors are overestimating the tightening to come. The swaps market is pricing a terminal rate in the region of 4.5% next year. Hiking by 75bp risks adding even more fuel to the fire, something we suspect the committee will be wary of doing, even if there are advantages in front-loading hikes. But even if the Bank doesn’t hike as far as markets expect, we do think the arrival of government stimulus means the BoE won’t be racing towards rate cuts next year, unlike some of its developed market counterparts.
Gilts, looking for some clarity
Gilts are looking for a much-needed reduction in uncertainty next week. Clearly, a 50bp hike would be a dovish surprise and help reverse some of the front-end’s weakness but even in the case of a 75bp move, the BoE clarifying its reaction function with regards to the energy package would be helpful. Fiscal and monetary policy competing with each other is an unnerving thought for bondholders. The Treasury’s fiscal event next week should also help answer any lingering questions about the size and financing of the energy support measures.
Gilts should widen to 200bp against Bund on a generous fiscal package
Even if the gilt ‘fear factor’ eases next week, it doesn’t answer the key question: who will buy all these gilts? A deficit-financed energy package will add to supply and to the BoE reducing the size of its portfolio. Private investors will have to make up the shortfall. This is not impossible but they will likely be some reluctance initially given the amount of new debt released into the market.
The BoE’s plan to start outright sales of gilts, albeit in small amounts initially, is an additional source of concern. On Thursday, the Bank is expected to vote in favour of starting this process, despite concerns about stress in the UK bond market.
Divergence in the size and financing of energy packages in the UK and the eurozone means the spread between 10Y gilts and bund should widen to 200bp.
This publication has been prepared by ING solely for information purposes irrespective of a particular user's means, financial situation or investment objectives. The information does not constitute investment recommendation, and nor is it investment, legal or tax advice or an offer or solicitation to purchase or sell any financial instrument. Read more
Download
Download article
